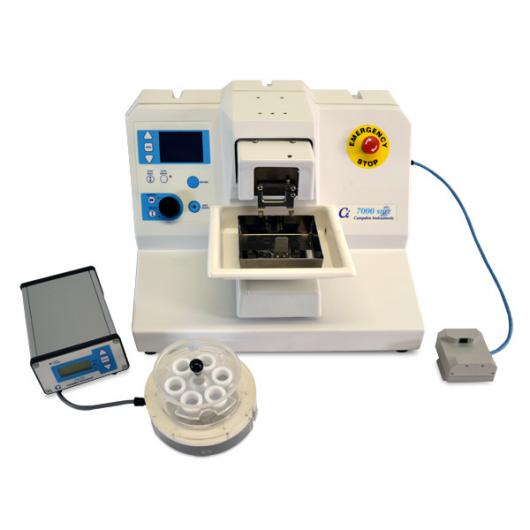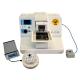

Vibrotome SMZ
A Campden csúcsminőségű, nagy pontosságú, rezgő mikrotómja (röviden vibrotóm) a világ legkiválóbb szövetmetszet-készítője a vizuális tapasz befogásához vagy a nagy felbontású képalkotáshoz készítendő preparációk esetén. A 7000smz-es sorozatú rezgő mikrotóm 10 éve számos laboratórium számára a kiválasztott műszer - több mint 450 laboratóriumban és ez még nem minden!
Főbb jellemzők
- Z tengelyes kalibráló egységet tartalmaz
- Z tengelyű pengeállító minimalizáló
- Pengetartó szöge a felhasználói igényekhez mérten
- A penge útja kezdő és befejező helyzetének beállítása
- Rezgési sebesség 50 és 120 Hz között
- 0,5 mm és 2,5 mm közötti amplitúdó
- Vezérelt pengeléptetés 10 mikron/sec sebességgel
- Kézi vagy automatikus működés
- "Automatikus" programozás az első metszet tárolásával
- A jeges vízfürdő tisztításhoz könnyen eltávolítható
- Opcióként LED-lámpa és mikroszkóp a tiszta megfigyeléshez
A Campden mikrotómok felhasználásával publikálták a neurológiai szövetek, a szív, a tüdő és a szövetállások vizuális javításához szükséges metszetek részletezését. A 7000smz-2 mikrotóm jelentős előrelépéseket jelent, nagyobb pontosságú, alacsonyabb költségek mellett.
A 7000smz-2 mikrotóm rezgő mechanizmusa soha nem látott pontosságot biztosít szinte csendes működéssel. Minden gépet kiszállítás előtt saját mérőeszközeinkkel tesztelünk, és minden gépet saját z-tengelyes kalibrációs ellenőrzővel látunk el.
A Z-tengely túlzott elhajlásának a szövetkészítmény egészségére és életképességére gyakorolt hatása Geiger et al (2003) publikációja óta sokat vitatott és a Campden 7000smz-2 szövetszeletelő pedig ≤ 1 µm Z-tengely elhajlással a vibrációs sebesség és amplitúdó széles tartományában, minden alkalommal egészséges életképes szakaszokat eredményez.
A felhasználói felület egyszerű és sokoldalú (a korábbi modellektől eltérően nincs lábkapcsoló), és egy gombnyomással egyszerű kezelhetősége, vagy számos változtatható paramétert kínál a szakértő felhasználó számára. A Campden 7000smz-2 szintén hosszú élettartamot biztosít, mivel a szeletelő nemcsak ≤ 1 µm teljesítményt biztosít, hanem a fejlett rezgő mechanizmus nem tartalmaz csapágyakat és más kopásnak kitett elemeket. Így az elkövetkező években is megőrzi a ≤ 1 µm z-ad teljesítményt, következetességet biztosítva a biológiai preparációban, anélkül, hogy költséges szervizelésre lenne szükség.
A szövet 4°C közeli hőmérsékleten tartásának a szeletelési folyamat során folyamatosnak kell lennie. Ez történhet passzív hűtéssel, ahol ismert mennyiségű jeget használnak a lehűlt a.c.s.f. fenntartására, vagy egy elektronikusan vezérelt hő-villamos szövetmosó hűtővel (7610A).
Campden mind a kerámia, mind a rozsdamentes acél mikrotóm pengéket kifejlesztette a gép mellett, így a penge élének csiszolási és csiszolási felületei illeszkednek a penge szövethez viszonyított lefelé irányuló tájolási szögéhez. A kerámia pengéknek különös előnyük van, ha 30 napnál régebbi agyszövetet szeletelnek. Ezeknek a kerámia mikrotóm lapátoknak van egy második előnyük is, mivel a rozsdamentes lapátokkal ellentétben ezeket nem kell minden szövetminta után cserélni.
További lehetőségek: LED hideg fény és nagyító, vagy a tiszta megfigyelés lehetősége szeletelés közben. Opcionális Slice inkubációs kamrával és hőmérséklet-szabályozóval látható.
- Szelvényvastagság lépésméret: 0,001 mm
- A mosóasztal emelkedési és esési sebessége: 1,0 mm/sec maximum
- A mosóasztal maximális (függőleges) mozgása: 19 mm
- Vágófej előrehaladási sebessége:
- Minimum: -4,0 mm/sec (-1,00 szeletelés közben)
- Maximum: +4,0 mm/sec (+1,00 szeletelés közben)
- Vágófej visszahúzási sebessége: 4,0 mm/sec
- A vágófej maximális útja: 40 mm
- Penge oszcillációs frekvenciája:
- Minimum: 50 Hz (alacsonyabb frekvenciák kérésre elérhetők)
- Maximum: 120 Hz (amplitúdótól függ)
- Frekvencia lépésmérete: 5 Hz
- A penge oszcillációs amplitúdója
- Minimum: 0,5 mm (névleges)
- Maximum: 2,5 mm (névleges)
- Amplitúdó lépésmérete: 0,25 mm (névleges)
- Teljesítményigény (választható): 115VAC 60Hz, 230VAC 50Hz
- Névleges teljesítmény: 100W
- Biztosíték teljesítménye
- 115V: T2A 250VAC
- 230V: T2A 250VAC
- Fényforrás: 100-240Vac 3W
- Méretek: 410 mm szélesség x 400 mm mélység x 270 mm magasság (fényforrás és mikroszkóp nélkül)
- Súly: 33 kg (mikroszkóp nélkül)
- Dobozos szállítási súly: 60 kg (mikroszkóp nélkül)
- 7550-1-CCampden Blades, ceramic - 5 pack
- 7550-1-SSCampden Blades, stainless steel - 50 pack
- 7000-3-1ACampden Bath mount for vibrating microtomes
- 7611ACampden Temperature controlled warming tissue bath
- CL200Campden Integrally mounted cold light source
- 7000-1-3Campden Integrally mounted magnifying glass
- 7000smz-CaseCampden Case for Campden 7000 series slicer
- 7000-1-60Campden Crate for 7000 series slicer
-
Preparation of viable adult ventricular myocardial slices from large and small mammals
Samuel A Watson, Martina Scigliano, Ifigeneia Bardi, Raimondo Ascione, Cesare M Terracciano & Filippo PerbelliniNature Protocols volume 12, pages 2623-2639 (2017) - Lásd absztrakt
-
Free-of-Acrylamide SDS-based Tissue Clearing (FASTClear) for three dimensional visualization of myocardial tissue
Filippo Perbellini, Alan K. L. Liu, Samuel A. Watson, Ifigeneia Bardi, Stephen M. Rothery & Cesare M. TerraccianoScientific Reports 7, Article number: 5188 (2017) - Lásd absztrakt
- Integraslice Bibliography
- Isolated Living Heart Slices from Adult Rats and Guinea Pgs as a Model for Drug Testing
- MEA recordings from acute heart slices from adult rats and guinea pigs
- Rhythmicity without Synchrony in the Electrically Uncoupled Inferior Olive
- NPL consultancy on oscillating movement featured it in their “Engineering Precisely” Newsletter
- Field and Action Potential Recordings in Heart Slices: Correlation with established In Vitro and In Vivo Models
- Cardiac tissue slices with prolonged survival for in vitro drug safety screening
- Innovation in safety pharmacology testing
- Methodological innovations expand the safety pharmacology horizon
- Campden Integraslice - Development of a lung slice preparation for recording ion channel activity in alveolar epithelial type 1 cells
- Nakano, T., Nakamura, Y., Irie, K., Okano, S., Morimoto, M., Yamashita, Y., … Mishima, K. (2020). Antithrombin gamma attenuates macrophage/microglial activation and brain damage after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Life Sciences, 252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117665
- Toft-Bertelsen, T. L., Larsen, B. R., Christensen, S. K., Khandelia, H., Waagepetersen, H. S., & MacAulay, N. (2020). Clearance of activity-evoked K+ transients and associated glia cell swelling occur independently of AQP4: A study with an isoform-selective AQP4 inhibitor. GLIA. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23851
- Vicente, M. C., Humphrey, C. M., Gargaglioni, L. H., & Ostrowski, T. D. (2020). Decreased excitability of locus coeruleus neurons during hypercapnia is exaggerated in the streptozotocin-model of Alzheimer’s disease. Experimental Neurology, 328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113250
- Vicente, M. C., Humphrey, C. M., Gargaglioni, L. H., & Ostrowski, T. D. (2020). Decreased excitability of locus coeruleus neurons during hypercapnia is exaggerated in the streptozotocin-model of Alzheimer’s disease. Experimental Neurology, 328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113250
- Sagoshi, S., Maejima, S., Morishita, M., Takenawa, S., Otubo, A., Takanami, K., … Ogawa, S. (2020). Detection and Characterization of Estrogen Receptor Beta Expression in the Brain with Newly Developed Transgenic Mice. Neuroscience, 438, 182–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.04.047
- Reisinger, S. N., Bilban, M., Stojanovic, T., Derdak, S., Yang, J., Cicvaric, A., … Pollak, D. D. (2020). Lmo3 deficiency in the mouse is associated with alterations in mood-related behaviors and a depression-biased amygdala transcriptome. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104480
- Brewer, C. L., Li, J., O’Conor, K., Serafin, E. K., & Baccei, M. L. (2020). Neonatal injury evokes persistent deficits in dynorphin inhibitory circuits within the adult mouse superficial dorsal horn. The Journal of Neuroscience, JN-RM- 0029-20. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0029-20.2020
- Stojanovic, T., Benes, H., Awad, A., Bormann, D., & Monje, F. J. (2020). Nicotine abolishes memory-related synaptic strengthening and promotes synaptic depression in the neurogenic dentate gyrus of miR-132/212 knockout mice. Addiction Biology. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12905
- Gu, Z., Koppel, N., Kalamboglas, J., Alexandrou, G., Li, J., Craig, C., … Yoshida, Y. (2020). Semaphorin-Mediated Corticospinal Axon Elimination Depends on the Activity-Induced Bax/Bak-Caspase Pathway. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 40(28), 5402–5412. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3190-18.2020
- Khatami, L., Safari, V., & Motamedi, F. (2020). Temporary inactivation of interpeduncular nucleus impairs long but not short term plasticity in the perforant-path dentate gyrus synapses in rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112212
- Genrikhs, E. E., Stelmashook, E. V., Voronkov, D. N., Novikova, S. V., Alexandrova, O. P., Fedorov, A. V., & Isaev, N. K. (2020). The single intravenous administration of methylene blue after traumatic brain injury diminishes neurological deficit, blood-brain barrier disruption and decrease in the expression of S100 protein in rats. Brain Research, 1740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146854
- Hart, E. E., Blair, G. J., O’Dell, T. J., Blair, H. T., & Izquierdo, A. (2019). Anterior cingulate cortex activity regulates effort- based decision making. BioRxiv, 005, 792069. https://doi.org/10.1101/792069
- Watson, S. A., Duff, J., Bardi, I., Zabielska, M., Atanur, S. S., Jabbour, R. J., … Terracciano, C. M. (2019). Biomimetic electromechanical stimulation to maintain adult myocardial slices in vitro. Nature Communications, 10(1), 2168. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10175-3
- Larsen, B. R., Stoica, A., & MacAulay, N. (2019). Developmental maturation of activity-induced K + and pH transients and the associated extracellular space dynamics in the rat hippocampus. Journal of Physiology, 597(2), 583–597. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP276768
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, I., Djebari, S., Temprano-Carazo, S., Vega-Avelaira, D., Jiménez-Herrera, R., Iborra-Lázaro, G., … Navarro-López, J. D. (2019). Hippocampal long-term synaptic depression and memory deficits induced in early amyloidopathy are prevented by enhancing G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel activity. Journal of Neurochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14946
- Brown, A. G., Thapa, M., Hooker, J. W., & Ostrowski, T. D. (2019). Impaired chemoreflex correlates with decreased c-Fos in respiratory brainstem centers of the streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease rat model. Experimental Neurology, 311, 285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.10.012
- Bartley, A. F., Abiraman, K., Stewart, L. T., Hossain, M. I., Gahan, D. M., Kamath, A. V., … Dobrunz, L. E. (2019). LSO:Ce Inorganic Scintillators Are Biocompatible With Neuronal and Circuit Function. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00024
- Pickford, J., Apps, R., & Bashir, Z. I. (2019). Muscarinic Receptor Modulation of the Cerebellar Interpositus Nucleus In Vitro. Neurochemical Research, 44(3), 627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2613-9
- Li, J., & Baccei, M. L. (2019). Neonatal Injury Alters Sensory Input and Synaptic Plasticity in GABAergic Interneurons of the Adult Mouse Dorsal Horn. The Journal of Neuroscience, 39(40), 7815–7825. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0509-19.2019
- Schappacher, K. A., Xie, W., Zhang, J. M., & Baccei, M. L. (2019). Neonatal vincristine administration modulates intrinsic neuronal excitability in the rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal dorsal horn during adolescence. Pain, 160(3), 645–657. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001444
- Ou, Q., Jacobson, Z., Abouleisa, R. R. E., Tang, X.-L., Hindi, S. M., Kumar, A., … Mohamed, T. M. A. (2019). Physiological Biomimetic Culture System for Pig and Human Heart Slices. Circulation Research, 125(6), 628–642. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.119.314996
- Díaz-García, C. M., Lahmann, C., Martínez-François, J. R., Li, B., Koveal, D., Nathwani, N., … Yellen, G. (2019). Quantitative in vivo imaging of neuronal glucose concentrations with a genetically encoded fluorescence lifetime sensor. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 97(8), 946–960. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24433
- Mohammed, U., Caine, R. S., Atkinson, J. A., Harrison, E. L., Wells, D., Chater, C. C., … Murchie, E. H. (2019). Rice plants overexpressing OsEPF1 show reduced stomatal density and increased root cortical aerenchyma formation. Scientific Reports, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41922-7
- Galloni, A. R., Laffere, A., & Rancz, E. A. (2019). Apical length modulates dendritic excitability in L5 pyramidal neurons.
- BioRxiv, 754499. https://doi.org/10.1101/754499
- Morris, P. G., Mishina, M., & Jones, S. (2018). Altered Synaptic and Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptor Properties in Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons From Mice Lacking the GluN2D Subunit. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00354
- Zhao, J., Baudry, M., & Jones, S. (2018). Calpain inhibition reduces NMDA receptor rundown in rat substantia nigra dopamine neurons. Neuropharmacology, 137, 221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.05.003
- Kammel, L. G., Wei, W., Jami, S. A., Voskuhl, R. R., & O’Dell, T. J. (2018). Enhanced GABAergic Tonic Inhibition Reduces Intrinsic Excitability of Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Cells in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience, 395, 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.11.003
- Brewer, C. L., & Baccei, M. L. (2018). Enhanced Postsynaptic GABA B Receptor Signaling in Adult Spinal Projection Neurons after Neonatal Injury. Neuroscience, 384, 329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.046
- Kawatani, M., Yamada, Y., & Kawatani, M. (2018). Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) action in the mouse area postrema neurons. Peptides, 107, 68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.07.010
- Murakami, T., Enjoji, M., & Koyama, S. (2018). Leptin attenuates D 2 receptor-mediated inhibition of putative ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons. Physiological Reports, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13631
- Ford, N. C., Ren, D., & Baccei, M. L. (2018). NALCN channels enhance the intrinsic excitability of spinal projection neurons. Pain, 159(9), 1719–1730. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000
- Khodai, T., Nunn, N., Worth, A. A., Feetham, C. H., Belle, M. D. C., Piggins, H. D., & Luckman, S. M. (2018). PACAP neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus are glucose inhibited and their selective activation induces hyperglycaemia. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 9(OCT). https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00632
- Saylor, D. M., Craven, B. A., Chandrasekar, V., Simon, D. D., Brown, R. P., & Sussman, E. M. (2018). Predicting patient exposure to nickel released from cardiovascular devices using multi-scale modeling. Acta Biomaterialia, 70, 304–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.024
- Morris, G., Brennan, G. P., Reschke, C. R., Henshall, D. C., & Schorge, S. (2018). Spared CA1 pyramidal neuron function and hippocampal performance following antisense knockdown of microRNA-134. Epilepsia, 59(8), 1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.14475
- Jiang, L., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Ma, D., & Wang, M. (2018). The Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin Type 1 Plays a Critical Role in Cortical Spreading Depression. Neuroscience, 382, 23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.025
- Murakami, T., Enjoji, M., & Koyama, S. (2018). Leptin attenuates D 2 receptor-mediated inhibition of putative ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons. Physiological Reports, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13631
- Romer, S. H., Seedle, K., Turner, S. M., Li, J., Baccei, M. L., & Crone, S. A. (2017). Accessory respiratory muscles enhance ventilation in ALS model mice and are activated by excitatory V2a neurons. Experimental Neurology, 287, 192–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.05.033
- Morris, G., Leite, M., Kullmann, D. M., Pavlov, I., Schorge, S., & Lignani, G. (2017). Cellular/Molecular Activity Clamp Provides Insights into Paradoxical Effects of the Anti-Seizure Drug Carbamazepine. Soc Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3697-16.2017
- Perbellini, F., Liu, A. K. L., Watson, S. A., Bardi, I., Rothery, S. M., & Terracciano, C. M. (2017). Free-of-Acrylamide SDS- based Tissue Clearing (FASTClear) for three dimensional visualization of myoca
- Tae, H. S., Smith, K. M., Phillips, A. M., Boyle, K. A., Li, M., Forster, I. C., … Reid, C. A. (2017). Gabapentin modulates HCN4 channel voltage-dependence. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8(AUG). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00554
- Watson, & Samuel. (2017). Preparation of viable adult ventricular myocardial slices from large and small mammals.
- Nature.Com. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.139
- Kang, C., Qiao, Y., Li, G., Baechle, K., Camelliti, P., Rentschler, S., & Efimov, I. R. (2016). Human Organotypic Cultured Cardiac Slices: New Platform For High Throughput Preclinical Human Trials. Sc
- Blot, A., de Solages, C., Ostojic, S., Szapiro, G., Hakim, V., & Léna, C. (2016). Time-invariant feed-forward inhibition of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex in vivo. Journal of Physiology, 594(10), 2729–2749. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP271518
- Hablitz, L. M., Molzof, H. E., Abrahamsson, K. E., Cooper, J. M., Prosser, R. A., Karen, X., & Gamble, L. (2015). Systems/Circuits GIRK Channels Mediate the Nonphotic Effects of Exogenous Melatonin. Soc Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1597-15.2015
- Larsen, B. R., Assentoft, M., Cotrina, M. L., Hua, S. Z., Nedergaard, M., Kaila, K., … Macaulay, N. (2014). Contributions of the Na+/K+-ATPase, NKCC1, and Kir4.1 to hippocampal K+ clearance and volume responses. GLIA, 62(4), 608–622. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22629
- Schoenberger, M., Damijonaitis, A., Zhang, Z., Nagel, D., & Trauner, D. (2014). Development of a New Photochromic Ion Channel Blocker via Azologization of Fomocaine. ACS Publications, 5(7), 514–518. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn500070w
- Yeoh, J. W., James, M. H., Graham, B. A., & Dayas, C. V. (2014). Electrophysiological characteristics of paraventricular thalamic (PVT) neurons in response to cocaine and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART). Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8(AUG). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00280
- Delerue, F., White, M., & Ittner, L. M. (2014). Inducible, tightly regulated and non-leaky neuronal gene expression in mice. Transgenic Research, 23(2), 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11
- Li, J., & Baccei, M. L. (2014). Neonatal tissue injury reduces the intrinsic excitability of adult mouse superficial dorsal horn neurons. Neuroscience, 256, 392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.057
- Guilmi, M. N. Di, Wang, T., Gonzalez Inchauspe, C., Forsythe, I. D., Ferrari, M. D., Van Den Maagdenberg, A. M. J. M., … Uchitel, O. D. (2014). Neurobiology of Disease Synaptic Gain-of-Function Effects of Mutant Ca v 2.1 Channels in a Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine Are Due to Increased Basal [Ca 2 ] i. Soc Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2526-13.2014
- Xiong, W., Chen, S. R., He, L., Cheng, K., Zhao, Y. L., Chen, H., … Zhang, L. (2014). Presynaptic glycine receptors as a potential therapeutic target for hyperekplexia disease. Nature Neuroscience 17, 232-239. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3615
- Hablitz, L. M., Molzof, H. E., Paul, J. R., Johnson, R. L., & Gamble, K. L. (2014). Suprachiasmatic nucleus function and circadian entrainment are modulated by G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying (GIRK) Channels. J. Physiol. 592.22, 5079-5092. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2014.282079
- Cameron, M. A., Suaning, G. J., Lovell, N. H., & Morley, J. W. (2013). Electrical Stimulation of Inner Retinal Neurons in Wild-Type and Retinally Degenerate (rd/rd) Mice. PLoS ONE, 8(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068882
- Wild, A. R., Akyol, E., Brothwell, S. L. C., Kimkool, P., Skepper, J. N., Gibb, A. J., & Jones, S. (2013). Memantine block depends on agonist presentation at the NMDA receptor in substantia nigra pars compacta dopamine neurones. Neuropharmcology 73, 138 – 146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.013
- Koyama, S., Kawaharada, M., Terai, H., Ohkurano, M., Mori, M., Kanamaru, S., & Hirose, S. (2013). Obesity decreases excitability of putative ventral tegmental area GABAergic neurons. Physiological Reports 1(5), 1-11 https://doi.org/10.1002/phy2.126
- Huang, S., & Uusisaari, M. Y. (2013). Physiological temperature during brain slicing enhances the quality of acute slice preparations Frontiers Neuroscience, 7.
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2013.00048/full
- Dougherty, S. E., Reeves, J. L., Lesort, M., Detloff, P. J., & Cowell, R. M. (2013). Purkinje cell dysfunction and loss in a knock-in mouse model of Huntington Disease. Experimental Neurology, 240(1), 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.11.015
- Dougherty, S. E., Reeves, J. L., Lesort, M., Detloff, P. J., & Cowell, R. M. (2013). Purkinje cell dysfunction and loss in a knock-in mouse model of Huntington Disease. Experimental Neurology,
- Puskarjov, M., Ahmad, F., Kaila, K., & Blaesse, P. (2012). Development/Plasticity/Repair Activity-Dependent Cleavage of the K-Cl Cotransporter KCC2 Mediated by Calcium-Activated Protease Calpain. Soc Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6265-11.2012
- Mewes, A., Franke, H., & Singer, D. (2012). Organotypic Brain Slice Cultures of Adult Transgenic P301S Mice-A Model for Tauopathy Studies. PLoS ONE, 7(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045017


